Anycast DNS
Find out how Anycast DNS can benefit you
Brief Summary
Anycast DNS is a networking technique that enables one IP address to apply to several servers. This means that the IP prefix is advertised from multiple locations. When you click on a link to visit a website, the network decides where to route your request based on routing protocols and the availability of servers.
Anycast DNS entails that any available DNS servers can respond to your request. As mentioned above, the response is based on protocols, availability, and location. Therefore, the closest server to your location will respond to your request. Anycast DNS has many benefits, and we’ll dive into them in this article.
Why does Anycast DNS stand out?
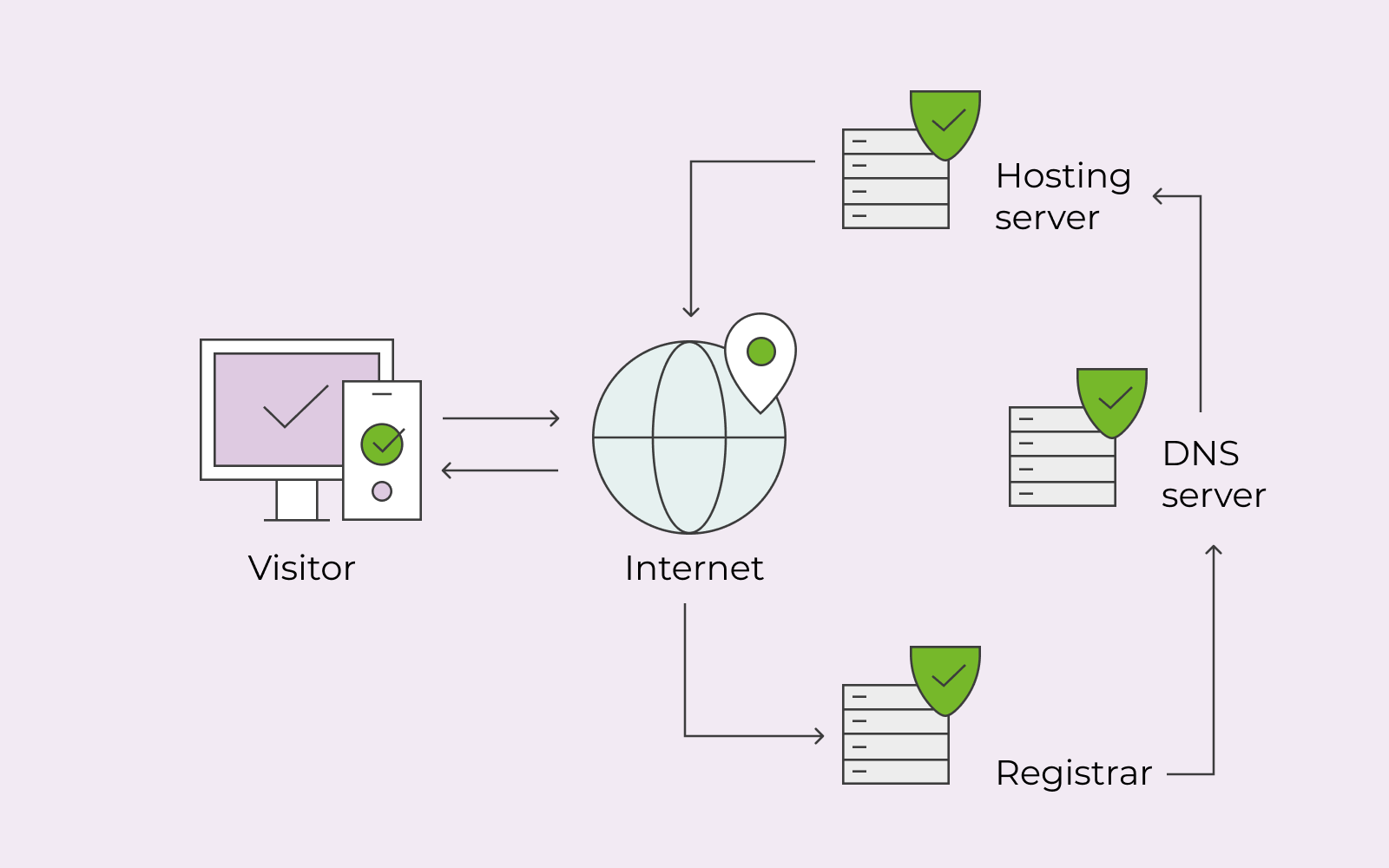
Usually, a server or device connects to the internet using an IP address (an IP address could be likened to a street address). Every device and server needs to have an IP address to be traceable and connect to the internet.
Typically it’s 1+1 when it regards IP addresses and the internet. This is because it goes from one device/server to the network.
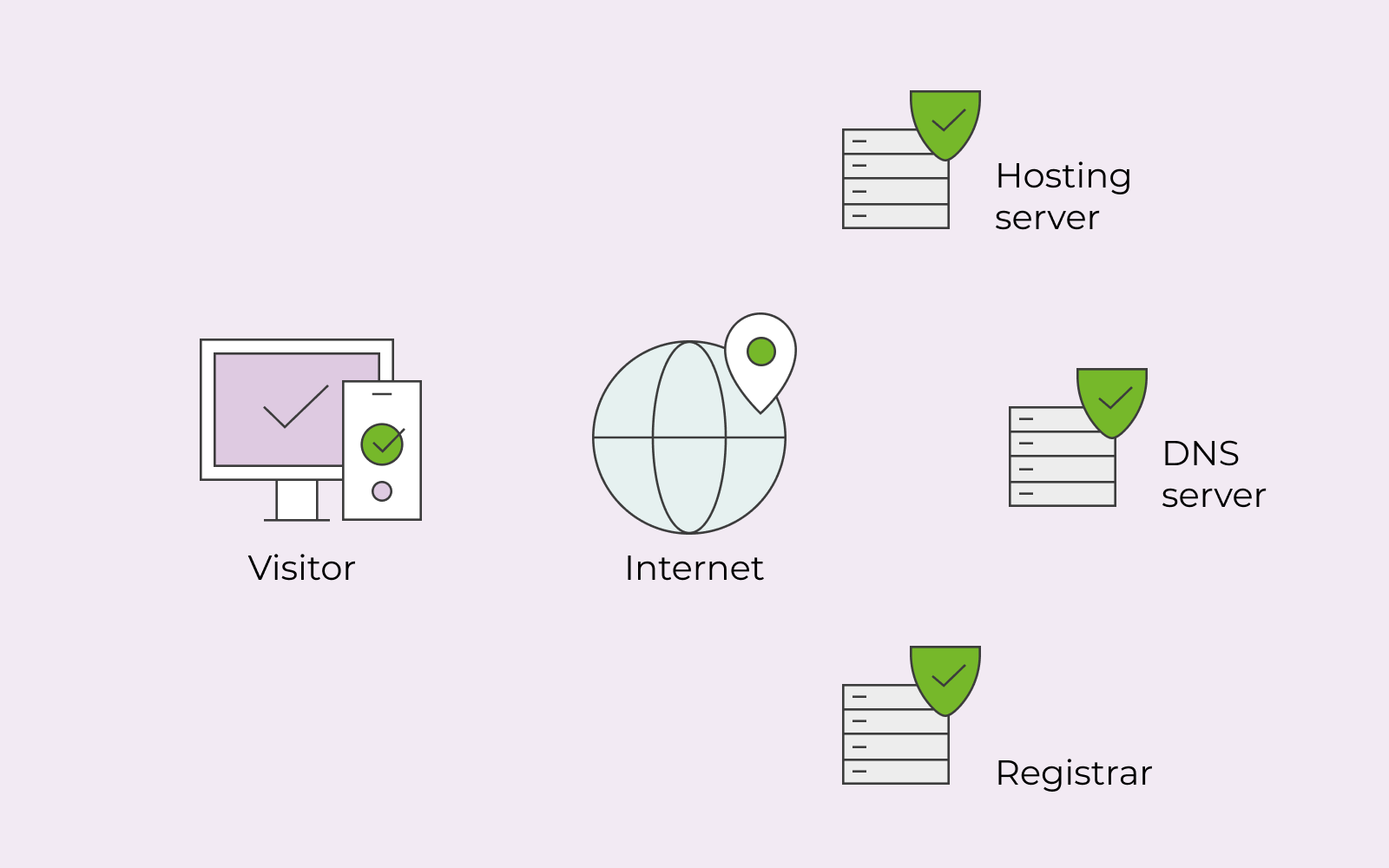
The differentiating point of Anycast DNS is that it allows multiple devices/servers, not just one, to connect to the internet using the same IP address. Thus, with Anycast DNS, it’s 1 + multiple servers/devices.
How does Anycast DNS work?
DNS, also known as Domain Name System, translates names. DNS translates, for example, your website’s name into an IP address so that machines can read the address. When a DNS translates various names, it’s referred to as resolving. Thus, if you hear or read about DNS resolver, it refers to servers working on the resolving.
When you send a query every time you visit a website, the request is sent to a DNS resolver that then returns the IP address of that website. So we type in, for example, www.one.com, but the machine will translate it into numbers so that you can visit the website.
What happens if I don’t have Anycast DNS?
If you don’t use Anycast DNS, it’ll slow down the process. You’re most likely using unicast routing if you’re not using Anycast DNS. Unicast operates differently than Anycast. Unicast will send the query to a specific server, not multiple ones. Subsequently, if the resolver is unavailable or does not work at the request time, the client will have to find a different way by sending queries to other DNS resolvers, affecting the time and speed.
Why use Anycast DNS?
Anycast DNS has many benefits; below, we’ll write three reasons for how it can benefit you.
- Latency
The way that Anycast DNS responds to queries and requests reduces the timeframe from when you as a user make a request to when the server responds to your request. Latency can be a problem because you’ll most likely want a response to your request immediately. As a user, you don’t want to wait for the website to load; you want the browser to load instantly.
Anycast DNS resolves latency, literally. Anycast DNS allows DNS resolving to work much faster because the query is sent to multiple DNS resolvers and not just a specific one. As the next and final step, it’ll find the closest DNS resolver available.
- Uptime
Anycast DNS improves uptime for the DNS resolving service. If you don’t use Anycast DNS, there’s a risk that the server you’re sending queries to is unavailable. Consequently, you’ll need to resolve the issue in other ways, leading to increased latency. However, if you use Anycast DNS, there’s a minimal chance of the same thing happening as the query will go to several servers. Thus, it’ll automatically choose a server that is both available and close to your device geographically.
- Protection
Anycast DNS will provide you with protection against DDoS attacks. DDoS attacks target DNS resolvers; this type of attack is called DNS flood. The army of bots will overwhelm the DNS resolver with an insane amount of DNS queries.
Anycast protects you from a DDoS attack by spreading the traffic. Instead of using one specific server, as mentioned above, Anycast DNS uses several servers, which makes it hard for the bot army to overwhelm the servers. The bot army can overwhelm or flood one server by sending unlimited queries; however, if Anycast DNS uses several servers, the army will not succeed.
